p300 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (F-4)
CAT.NO. : ARA0304
RMB Please choose
RMB Please choose
Size:
Trail, Bulk size or Custom requests Please contact us
*产品价格可能会有所调整,请以品牌方官网实时更新的价格为准,以确保准确性。
BACKGROUND
Cyclic AMP - regulated gene expression frequently involves a DNA element designated the cAMP - regulated enhancer (CRE). Many transcription factors bind to this element, including the protein CREB which is activated as a result of phosphorylation by protein kinase A. It has been shown that protein kinase A - mediated CREB phosphorylation results in its binding to a nuclear protein designated CBP (for CREB - binding protein). These findings suggest that CBP has many of the properties expected of a CREB co - activator. Another high molecular weight transcriptional adapter protein, designated p300, is characterized by three cysteine and histidine - rich regions, of which the most carboxy - terminal region specifically binds the adenovirus E1A protein. p300 molecules lacking an intact E1A binding site bypass E1A repression even in the presence of high concentrations of E1A. Sequence analysis of CBP and p300 has revealed substantial homology, arguing that these proteins are members of a conserved family of co - activators.
Application
p300 (F-4) is recommended for detection of p300 of mouse, rat and human origin by Western Blotting (starting dilution 1:100, dilution range 1:100 - 1:5000), immunoprecipitation [1 - 2 µg per 100 - 500 µg of total protein (1 ml of cell lysate)], immunofluorescence (starting dilution 1:50, dilution range 1:50 - 1:500), immunohistochemistry (including paraffin - embedded sections) (starting dilution 1:50, dilution range 1:50 - 1:500) and solid phase ELISA (starting dilution 1:30, dilution range 1:30 - 1:3000).
Data
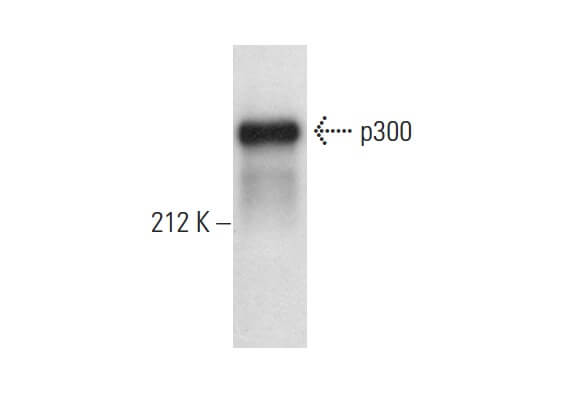
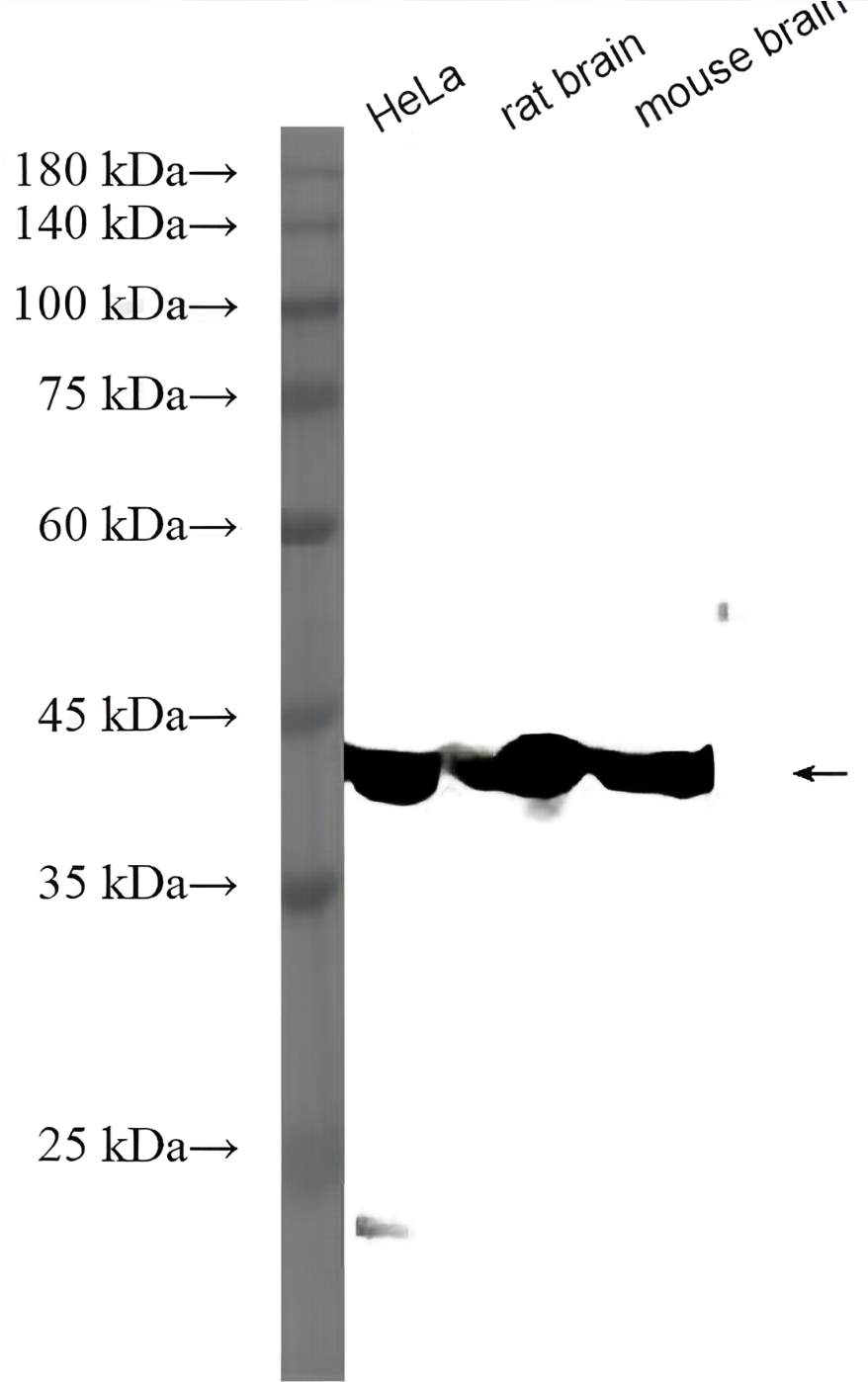
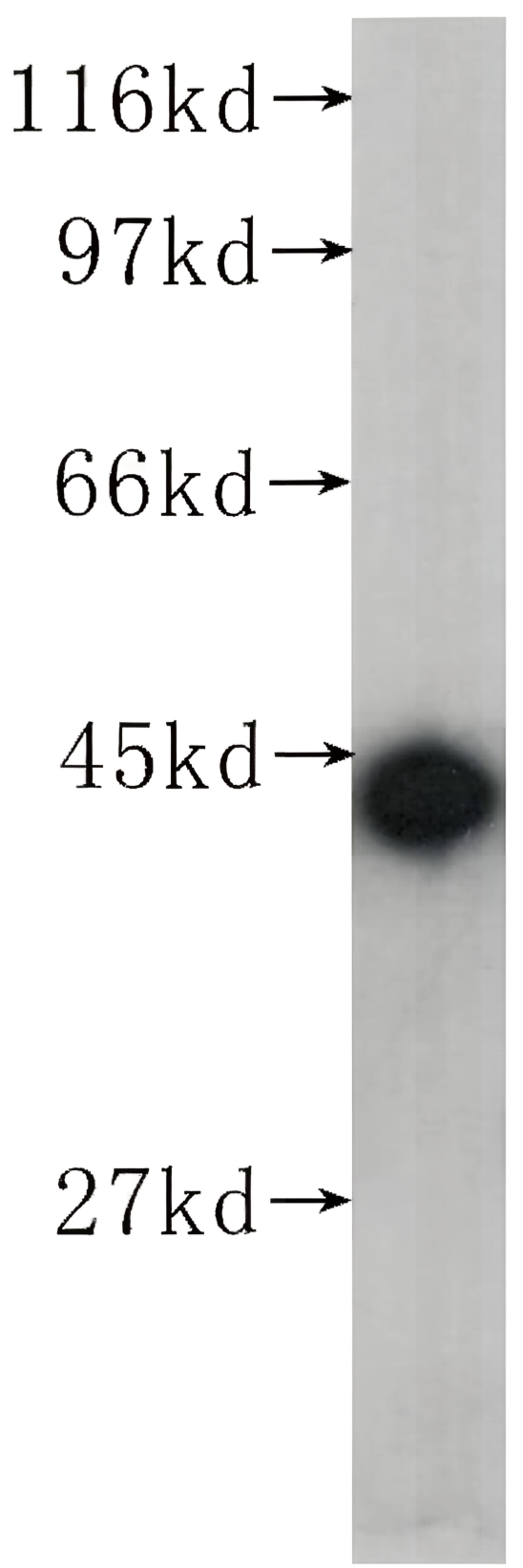
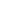
p300 (F-4). Western blot analysis of p300 expression in Jurkat (A) and MCF7 (B) nuclear extracts
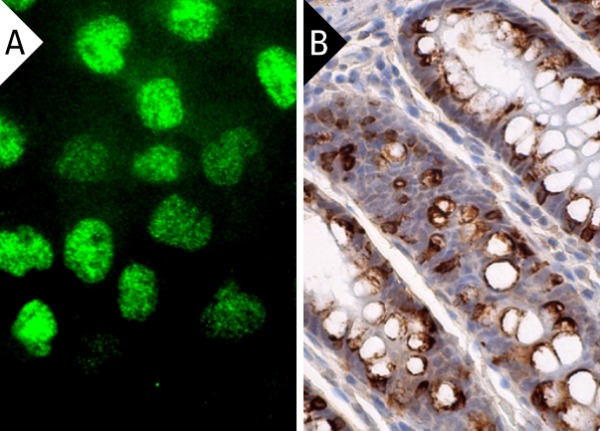
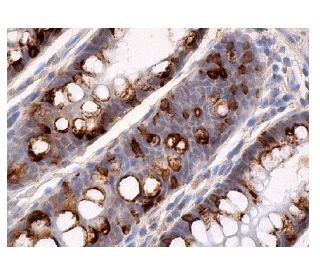
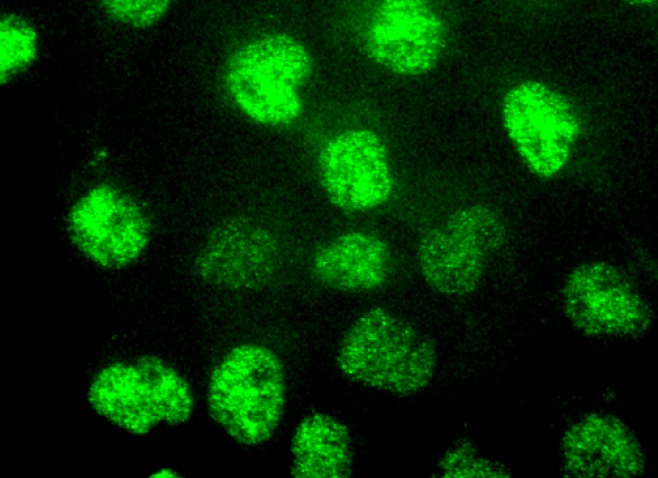
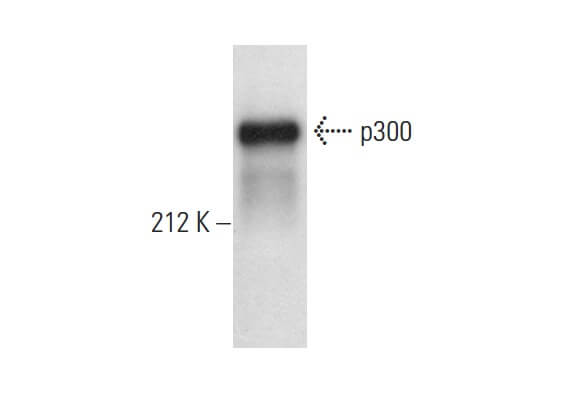
p300 (F-4). Immunofluorescence staining of formalin-fixed A-431 cells showing nuclear localization (A). Immunoperoxidase staining of formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded human rectum tissue showing nuclear and cytoplasmic staining of subset of glandular cells (B).
 New Products
New Products




 Datasheet
Datasheet