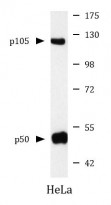
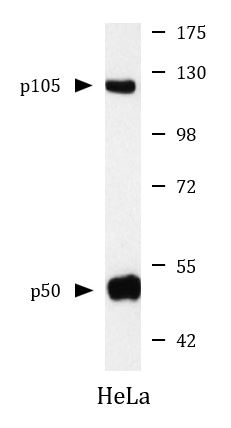
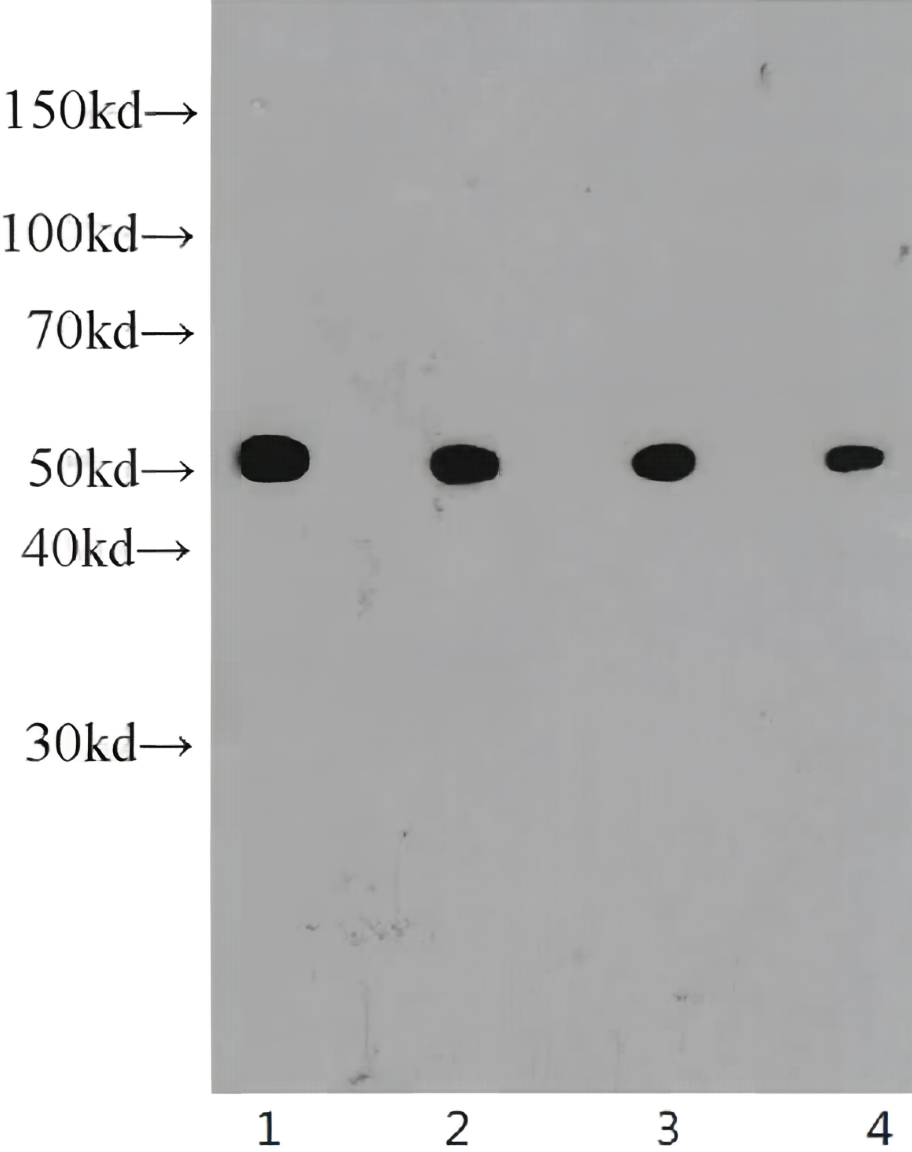
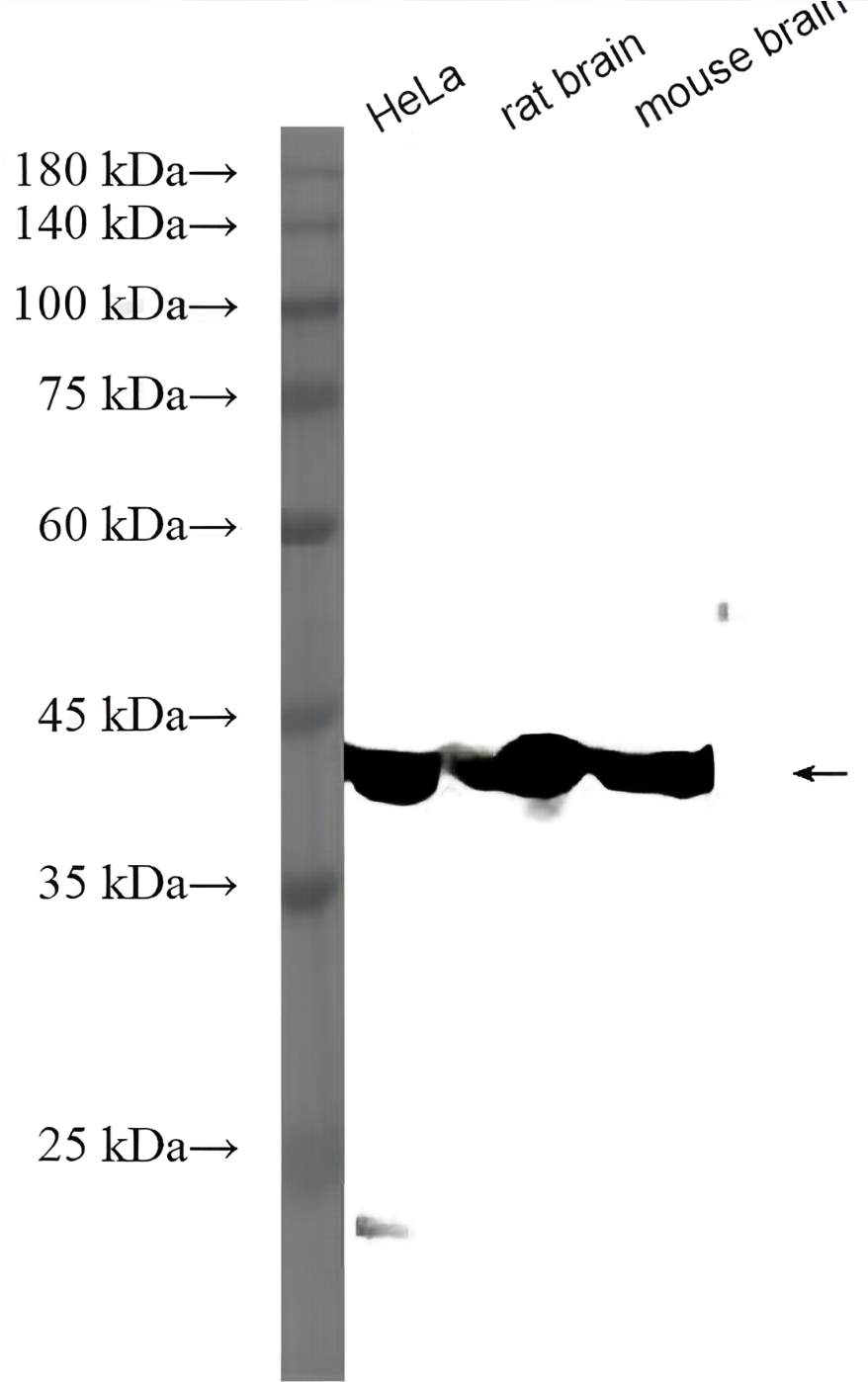
anti-NFkB p105 / p50 antibody
CAT.NO. : ARG55912
US$ Please choose
US$ Please choose
Size:
Trail, Bulk size or Custom requests Please contact us
*产品价格可能会有所调整,请以品牌方官网实时更新的价格为准,以确保准确性。
概述
| 产品描述 | Mouse Monoclonal antibody recognizes NFkB p105 / p50 |
|---|---|
| 反应物种 | Hu, Ms, Rat |
| 应用 | WB |
| 宿主 | Mouse |
| 克隆 | Monoclonal |
| 同位型 | IgG1 |
| 靶点名称 | NFkB p105 / p50 |
| 抗原物种 | Human |
| 抗原 | Recombinant Human NFkB p105 / p50 protein. |
| 偶联标记 | Un-conjugated |
| 別名 | NF-kB1; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit; NFkappaB; p105; EBP-1; NF-kappa-B; NF-kappaB; NFKB-p50; KBF1; DNA-binding factor KBF1; p50; NFKB-p105 |
应用说明
| 应用建议 |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 应用说明 | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. | ||||
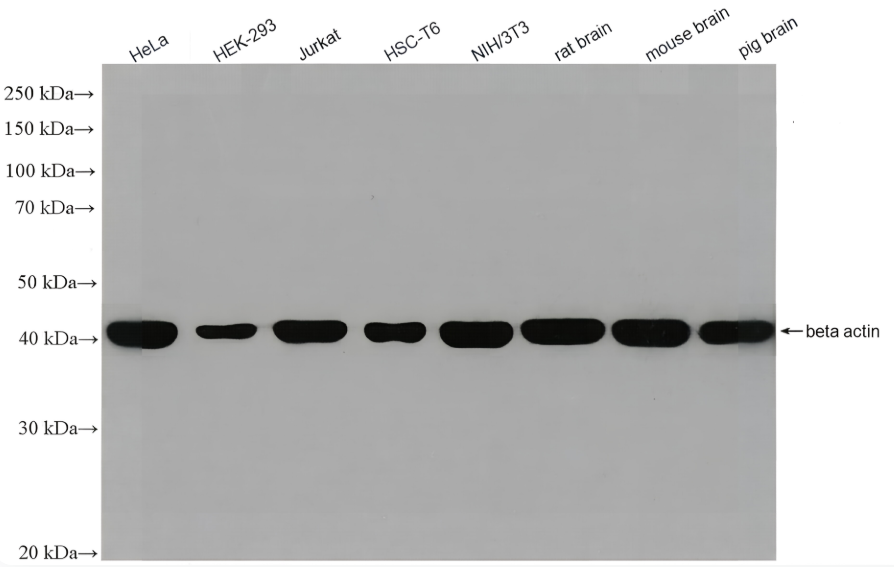
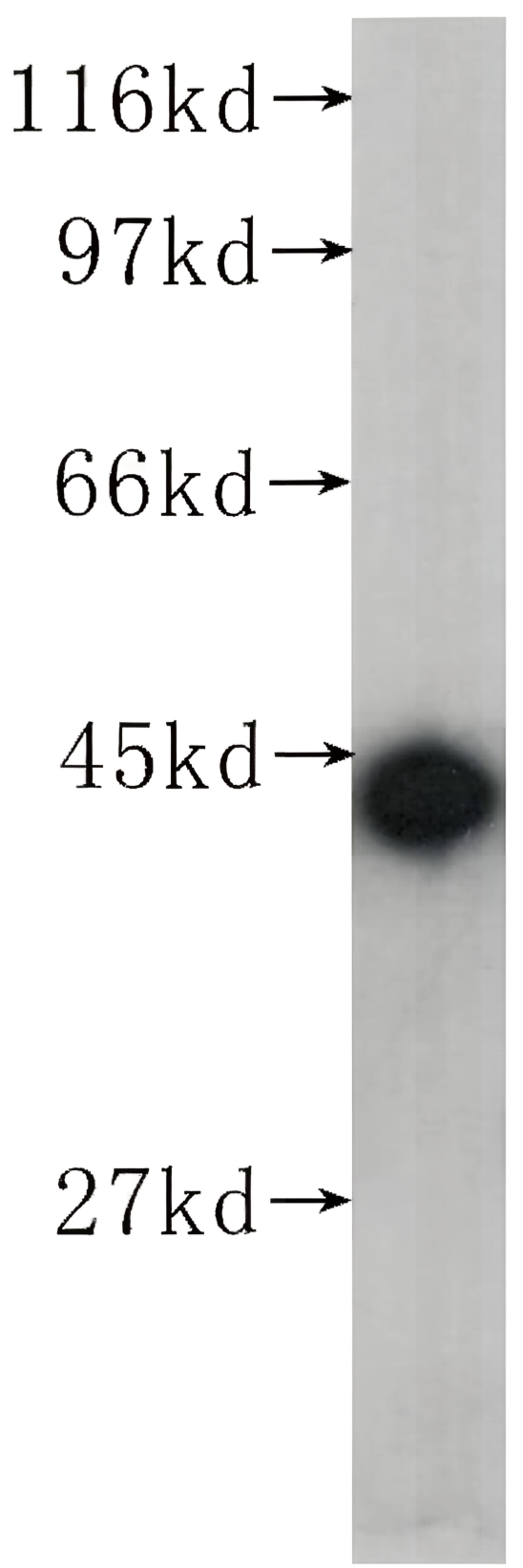
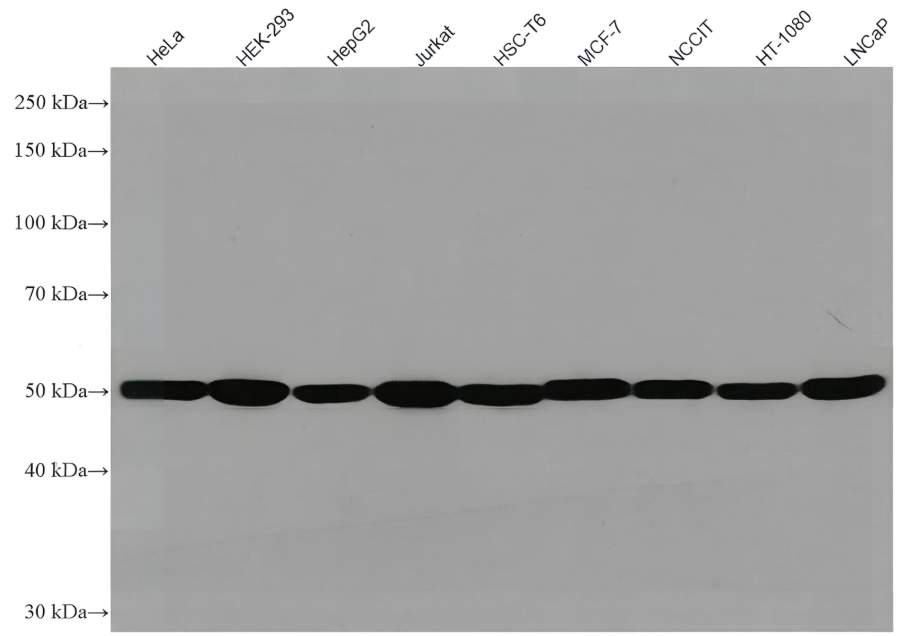
| 实际分子量 | 120, 50 kDa |
属性
| 形式 | Liquid |
|---|---|
| 缓冲液 | PBS (pH 7.4), 0.03% Proclin-300 and 50% Glycerol |
| 抗菌剂 | 0.03% Proclin-300 |
| 稳定剂 | 50% Glycerol |
| 存放说明 | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| 注意事项 | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
生物信息
| 数据库连接 | Swiss-port # P19838 Human Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit Swiss-port # P25799 Mouse Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
|---|---|
| 基因名称 | NFKB1 |
| 全名 | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 |
| 背景介绍 | This gene encodes a 105 kD protein which can undergo cotranslational processing by the 26S proteasome to produce a 50 kD protein. The 105 kD protein is a Rel protein-specific transcription inhibitor and the 50 kD protein is a DNA binding subunit of the NF-kappa-B (NFKB) protein complex. NFKB is a transcription regulator that is activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant-free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. Activated NFKB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions. Inappropriate activation of NFKB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NFKB leads to inappropriate immune cell development or delayed cell growth. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] |
| 生物功能 | NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and RelB-p50 complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p50-p50 homodimer is a transcriptional repressor, but can act as a transcriptional activator when associated with BCL3. NFKB1 appears to have dual functions such as cytoplasmic retention of attached NF-kappa-B proteins by p105 and generation of p50 by a cotranslational processing. The proteasome-mediated process ensures the production of both p50 and p105 and preserves their independent function, although processing of NFKB1/p105 also appears to occur post-translationally. p50 binds to the kappa-B consensus sequence 5'-GGRNNYYCC-3', located in the enhancer region of genes involved in immune response and acute phase reactions. In a complex with MAP3K8, NFKB1/p105 represses MAP3K8-induced MAPK signaling; active MAP3K8 is released by proteasome-dependent degradation of NFKB1/p105. [UniProt] |
| 细胞定位 | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor. |
| 研究领域 | Cancer antibody; Cell Biology and Cellular Response antibody; Cell Death antibody; Gene Regulation antibody; Immune System antibody; Signaling Transduction antibody; NFkB nuclear translocation Study antibody |
| 预测分子量 | 105, 50 kDa |
| 翻译后修饰 | While translation occurs, the particular unfolded structure after the GRR repeat promotes the generation of p50 making it an acceptable substrate for the proteasome. This process is known as cotranslational processing. The processed form is active and the unprocessed form acts as an inhibitor (I kappa B-like), being able to form cytosolic complexes with NF-kappa B, trapping it in the cytoplasm. Complete folding of the region downstream of the GRR repeat precludes processing. Phosphorylation at 'Ser-903' and 'Ser-907' primes p105 for proteolytic processing in response to TNF-alpha stimulation. Phosphorylation at 'Ser-927' and 'Ser-932' are required for BTRC/BTRCP-mediated proteolysis. Polyubiquitination seems to allow p105 processing. S-nitrosylation of Cys-61 affects DNA binding. The covalent modification of cysteine by 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin-J2 is autocatalytic and reversible. It may occur as an alternative to other cysteine modifications, such as S-nitrosylation and S-palmitoylation. |
 New Products
New Products