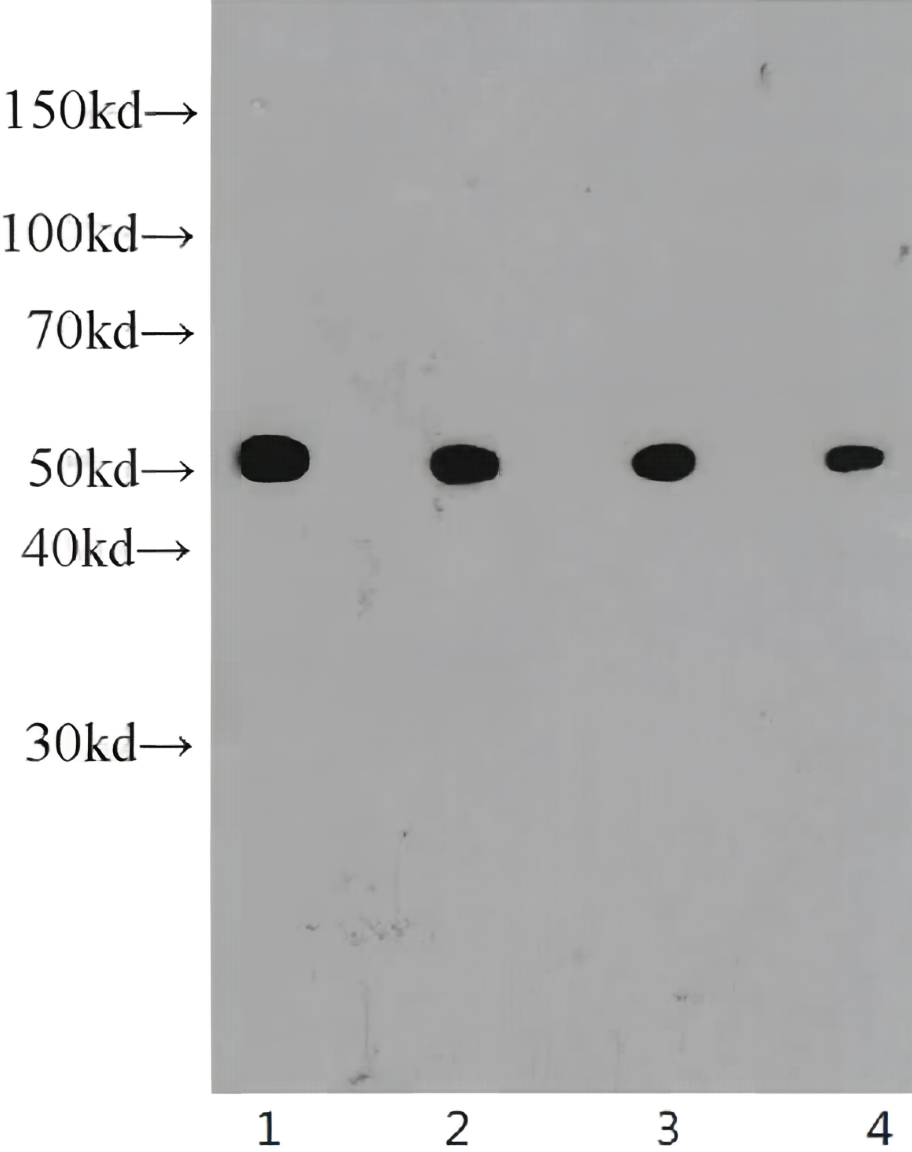
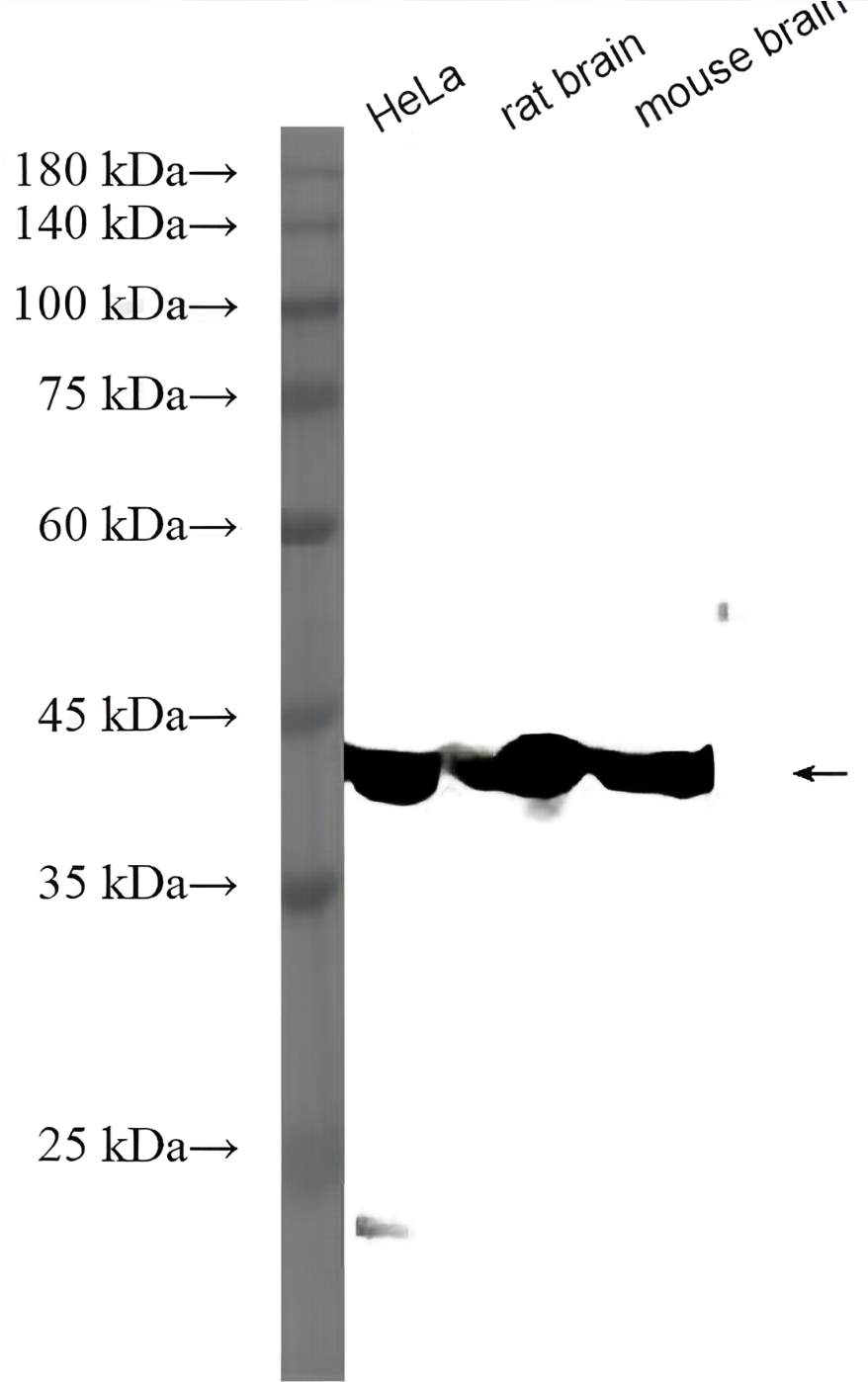
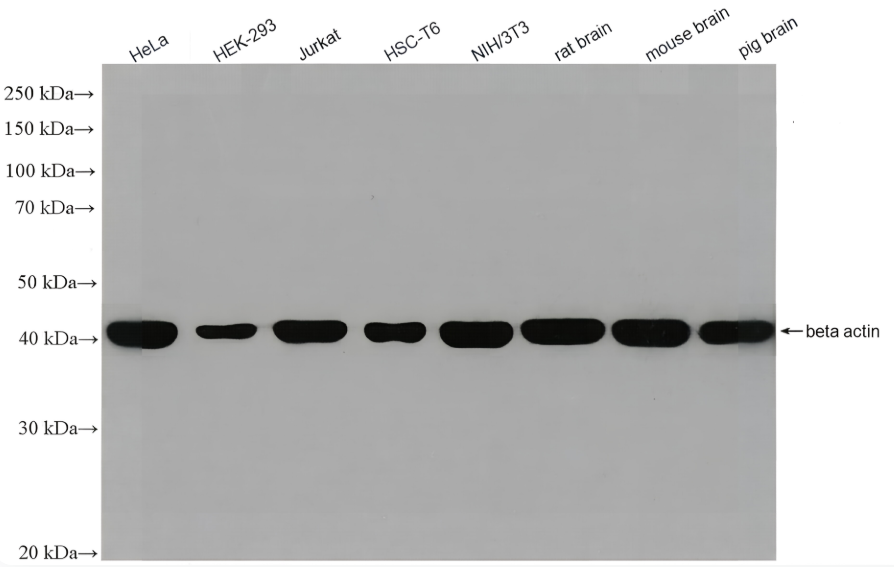
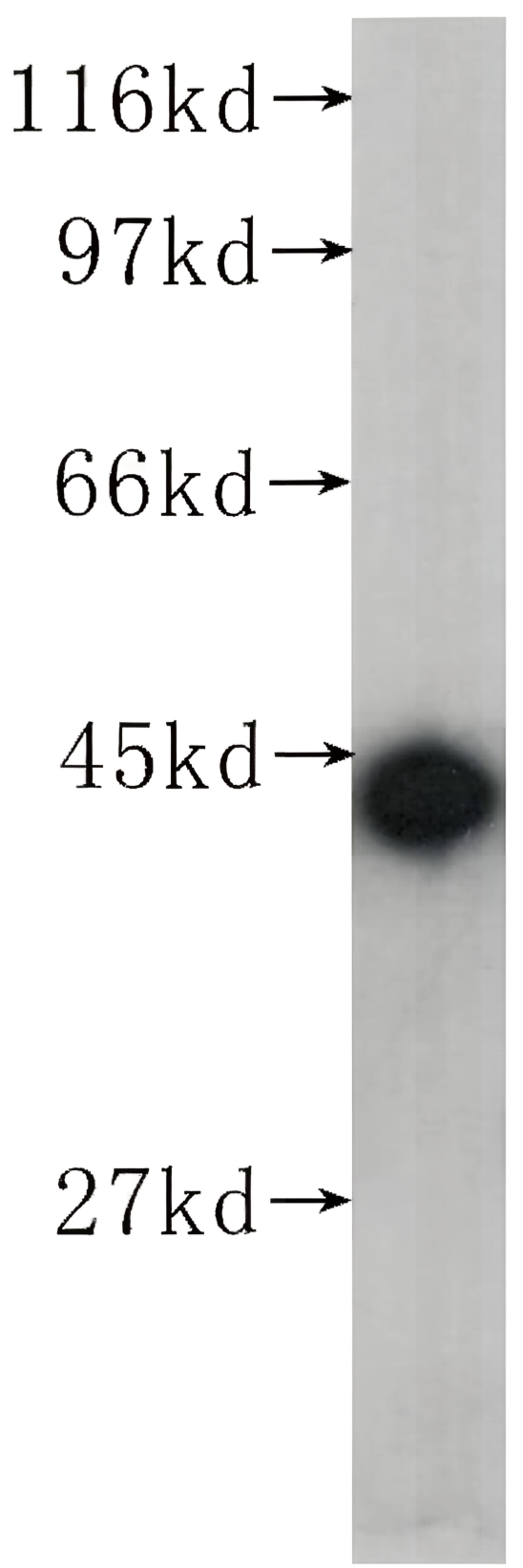
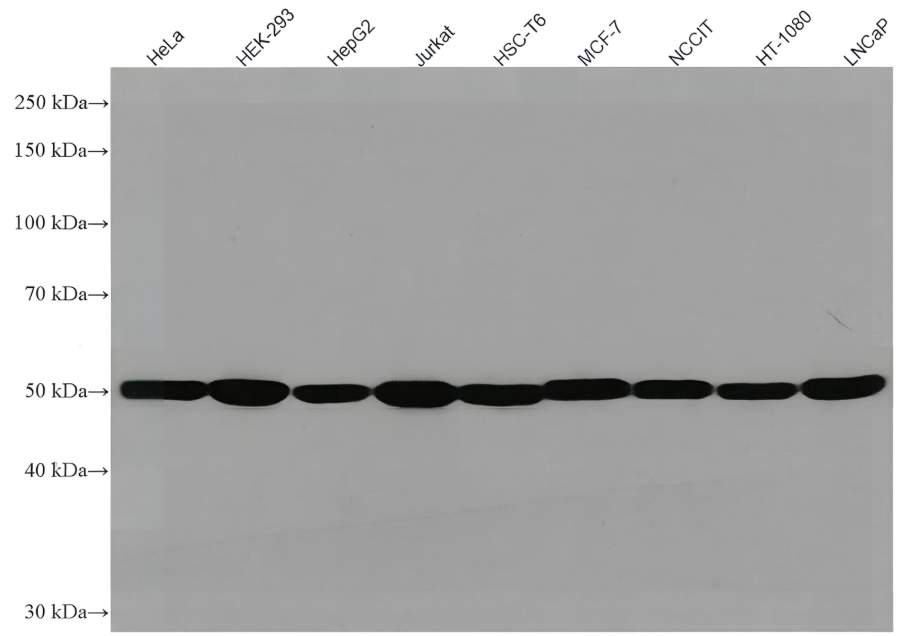
anti-NuMA antibody [A73-B/D12]
CAT.NO. : ARG62359
US$ Please choose
US$ Please choose
Size:
Trail, Bulk size or Custom requests Please contact us
*产品价格可能会有所调整,请以品牌方官网实时更新的价格为准,以确保准确性。
概述
| 产品描述 | Mouse Monoclonal antibody [A73-B/D12] recognizes NuMA |
|---|---|
| 反应物种 | Hu |
| 应用 | IHC-Fr, IHC-P, IP, WB |
| 宿主 | Mouse |
| 克隆 | Monoclonal |
| 克隆号 | A73-B/D12 |
| 同位型 | IgM |
| 靶点名称 | NuMA |
| 抗原物种 | Human |
| 抗原 | Raised against Ls 174T cell line of human origin |
| 偶联标记 | Un-conjugated |
| 別名 | SP-H antigen; Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1; NMP-22; NUMA; Nuclear matrix protein-22; NuMA protein |
应用说明
| 应用建议 |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 应用说明 | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. | ||||||||||
| 阳性对照 | Tonsil, Thymus, Spleen |
属性
| 形式 | Liquid |
|---|---|
| 纯化 | Purified Antibody |
| 缓冲液 | 1X PBS and 0.1% Sodium azide |
| 抗菌剂 | 0.1% Sodium azide |
| 浓度 | 0.2 mg/ml |
| 存放说明 | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or below. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| 注意事项 | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
生物信息
| 数据库连接 | Swiss-port # Q14980 Human Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 |
|---|---|
| 基因名称 | NUMA1 |
| 全名 | nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 |
| 背景介绍 | This gene encodes a large protein that forms a structural component of the nuclear matrix. The encoded protein interacts with microtubules and plays a role in the formation and organization of the mitotic spindle during cell division. Chromosomal translocation of this gene with the RARA (retinoic acid receptor, alpha) gene on chromosome 17 have been detected in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2013] |
| 生物功能 | Highly abundant component of the nuclear matrix where it may serve a non-mitotic structural role, occupies the majority if the nuclear volume. Required for maintenance and establishment of the mitotic spindle poles, functionning as a tether linking bulk microtubules of the spindle to centrosomes. May be involved in coordination of the alignment of the mitotic spindle to the cellular polarity axis, which is a prerequisite for asymmetric cell divisions. [UniProt] |
| 研究领域 | Cell Biology and Cellular Response antibody |
| 预测分子量 | 238 kDa |
| 翻译后修饰 | Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation on Thr-2055 regulates the extent of cortical NUMA1 and the dynein-dynactin complex localization during mitotic metaphase and anaphase (PubMed:23921553). In metaphase, phosphorylation on Thr-2055 occurs in a kinase CDK1-dependent manner; this phosphorylation maintains low levels of cortical dynein-dynactin complex at metaphase, and hence proper spindle positioning (PubMed:7769006, PubMed:23921553, PubMed:24371089). In anaphase, dephosphorylated on Thr-2055 by phosphatase PPP2CA; this dephosphorylation stimulates its membrane association and with the dynein-dynactin complex its enrichment at the cell cortex, and hence robust spindle elongation (PubMed:23921553, PubMed:24371089). Probably also phosphorylated on Thr-2015 and Ser-2087 by CDK1; these phosphorylations may regulate its cell cortex recruitment during metaphase and anaphase (PubMed:23870127). Phosphorylated on Thr-1047, Ser-1769, Ser-1772, Ser-1789 and Ser-1834 by PLK1; these phosphorylations induce cortical dynein-dynactin complex dissociation from the NUMA1-GPSM2 complex and negatively regulates cortical dynein-dynactin complex localization (PubMed:22327364). ADP-ribosylated by TNKS at the onset of mitosis; ADP-ribosylation is not required for its localization to spindle poles (PubMed:16076287). O-glycosylated during cytokinesis at sites identical or close to phosphorylation sites, this interferes with the phosphorylation status (PubMed:20068230). Ubiquitinated with 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. Deubiquitination by the BRISC complex is important for the incorporation of NUMA1 into mitotic spindle poles and normal spindle pole function, probably by modulating interactions between NUMA1, dynein-dynactin complex and importin-beta. |
 New Products
New Products




![anti-NuMA antibody [A73-B/D12]](/upload/image/20241105/8415bc38bc270b898ee2a90369a6c7fb.jpg)