Human G-CSF ELISA Kit
CAT.NO. : AEH0149
RMB Please choose
RMB Please choose
Size:
Trail, Bulk size or Custom requests Please contact us
*产品价格可能会有所调整,请以品牌方官网实时更新的价格为准,以确保准确性。
Background
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is a 24-25 kDa monomeric glycoprotein that regulates the proliferation, differentiation, and activation of hematopoietic cells in the neutrophilic granulocyte lineage. Mature human G-CSF is a 178 amino acid (aa) O-glycosylated protein that contains two intrachain disulfide bridges. In humans, alternate splicing generates a second minor isoform with a 3 aa deletion. Mouse and human G-CSF share 76% aa sequence identity, and the two proteins show species cross-reactivity. G-CSF is produced by activated monocytes and macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, astrocytes, neurons, and bone marrow stroma cells. In addition, various tumor cells express G-CSF constitutively. Human G-CSF receptor (G-CSF R) is a 120 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the hematopoietin receptor superfamily. The mature protein consists of a 603 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 23 aa transmembrane segment, and a 186 aa cytoplasmic domain. The ECD contains an N-terminal Ig-like domain, a cytokine receptor homology domain, and three fibronectin type III domains. Alternate splicing of human G-CSF R generates additional isoforms including a potentially soluble form of the receptor. The ECDs of mouse and human G-CSF R share 63% aa sequence identity. G-CSF R forms a complex with the ligand in a 2:2 ratio. It is expressed on monocytes, neutrophils, megakaryocytes, platelets, myeloid progenitors, trophoblasts and placenta, endothelial cells, and various tumor cell types. G-CSF is an important regulator for granulopoiesis in vivo, and mutations in G-CSF R are associated with congenital neutropenia. G-CSF can support the growth of multilineage hematopoietic progenitor cells and mobilize them from the bone marrow into the bloodstream. G-CSF enhances the functional capacity of mature neutrophils and supports their survival by limiting the rate of apoptosis. G-CSF also enhances M-CSF induced monocytopoiesis from hematopoietic progenitor cells and stimulates the proliferation of peripheral Th2-inducing dendritic cells. It promotes the development of T cell immune tolerance as well as tissue recovery following myocardial infarction and cerebral ischemia.
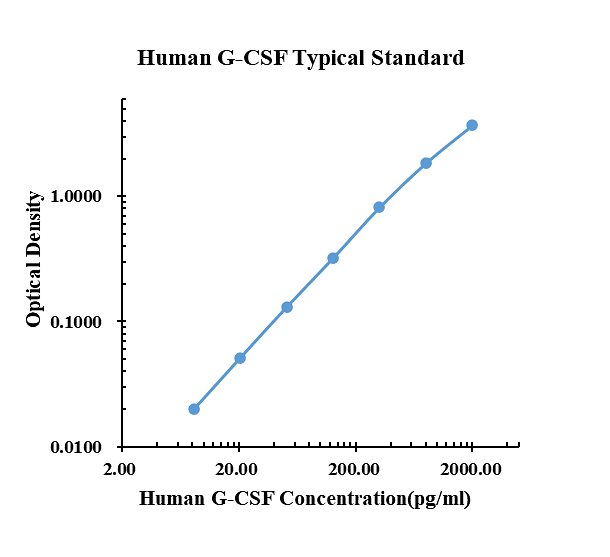
Typical data
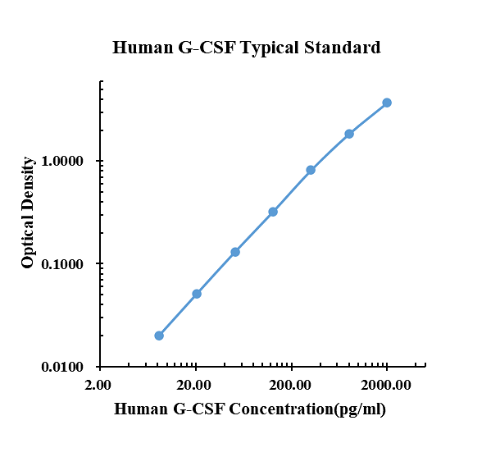
|
pg/ml |
O.D. |
Average |
Corrected |
|
|
0.00 |
0.0148 |
0.0144 |
0.0146 |
|
|
8.19 |
0.0336 |
0.0353 |
0.0345 |
0.0199 |
|
20.48 |
0.0645 |
0.0670 |
0.0658 |
0.0512 |
|
51.20 |
0.1376 |
0.1524 |
0.1450 |
0.1304 |
|
128.00 |
0.3456 |
0.3250 |
0.3353 |
0.3207 |
|
320.00 |
0.8238 |
0.8329 |
0.8284 |
0.8138 |
|
800.00 |
1.7270 |
1.9720 |
1.8495 |
1.8349 |
|
2000.00 |
3.5990 |
3.7930 |
3.6960 |
3.6814 |
Precision
|
Intra-assay Precision |
Inter-assay Precision |
|||||
|
Sample Number |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
|
22 |
22 |
22 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
|
|
Average(pg/ml) |
49.6 |
227.9 |
737.9 |
43.6 |
210.6 |
661.4 |
|
Standard Deviation |
2.9 |
6.7 |
49.3 |
1.2 |
9.5 |
18.9 |
|
Coefficient of Variation(%) |
5.9 |
2.9 |
6.7 |
2.6 |
4.5 |
2.9 |
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays) Three samples of known concentration were tested six times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Spike Recovery
The spike recovery was evaluated by spiking 3 levels of human G-CSF into health human serum sample. The un-spiked serum was used as blank in this experiment. The recovery ranged from 80% to 119% with an overall mean recovery of 101%.
Sample Values
|
Sample Matrix |
Sample Evaluated |
Range (pg/ml) |
Detectable (%) |
Mean of Detectable (pg/ml) |
|
Serum |
30 |
0.72-42.44 |
100 |
6.93 |
 New Products
New Products




 Protocol Booklet
Protocol Booklet